
Ref : Google Images
A satellite is one of the most complex machines ever built by mankind. It is a great challenge to make a satellite because of the harsh conditions of space, the shock waves, vibrations of launch, the varying temperatures (from -250 degrees to > 100 degrees warm), making adjustments in the orbit and dealing with space debris, solar flare and radiation, making it last for about 5-10 years. Sophisticated electronics are used which can withstand these harsh conditions, Apart from it there are no repair/ reservice options either – one part damaged or malfunctioned , then goodbye satellite forever..!!

Ref : Google Images
It has its own communication system module often termed as payload to receive the signal from earth (UPLINK) and filters the signal from noisy components, amplify it and send it back to earth where an antenna receives the signal (DOWNLINK). It does this work with the help of a transponder, which is an integrated radio signal receiver and antenna. The frequency is generated by a quartz resonator, which is the heart of satellite.
Classification of Satellites :
Satellites are orbiting the earth in three different orbits : Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) and Geosynchronus Earth Orbit(GEO).LEO satellites work at an altitude between 160 km and 1,600 km above Earth. MEO satellites operate from 10,000 to 20,000 km .GEO satellites are positioned 35,786 km (22,236 miles) above Earth and they complete one orbit in 24 hours.

Ref : Google images
LEO Satellites
- Advantages:
- Reduces transmission delay
- Eliminates need for bulky receiving equipment.
- Disadvantages:Subdivisions: Little, Big, and Mega (Super) LEOs.
- Smaller coverage area.
- Shorter life span (5-8 yrs.) than GEOs (10 yrs).
Little LEO Satellite
- 0.8 GHz range
- Small, low-cost
- Vehicle tracking, environmental monitoring and two-way data communication. Used for short, narrowband communications.
Super LEO Satellite
- 2 GHz or above range
- Can offer global services, which can be subject to regulatory requirements.
- Used for technology devices such as high-speed, high-bandwidth data communications, and video conferencing. They carry voice and high-speed data services. The main uses are data communications and real-time voice delivery to hand-held devices.
MEO Satellite :
- MEO satellites have a larger coverage area than LEO satellites
- A MEO satellite’s longer duration of visibility and wider footprint means fewer satellites are needed in a MEO network than a LEO network
- A MEO satellite’s distance gives it a longer time delay and weaker signal than a LEO satellite, though not as bad as a GEO satellite
Satellite use very high frequency range of signals for effective communications. The lower GHz frequency range bands are L band,S band, C band extending upto Ku,Ka, X and Vbands which extend upto 50GHz range. The L,S,C bands have low power and Ku,Ka, X and V bands have high power.
GEO Satellite :
- Orbit is synchronous with the earth’s rotation.
- From the ground the satellite appears fixed.
- Altitude is about 23,000 miles.
- Coverage to 40% of planet per satellite.
- Geostationary satellites are commonly used for communications and weather-observation.
- The typical service life expectancy of a geostationary satellite is 10-15 years.
- Because geostationary satellites circle the earth at the equator, they are not able to provide coverage at the Northernmost and Southernmost latitudes.
- Advantages:
- Weather images can be displayed.
- Television broadcasts are uninterrupted.
- Used to track major developments such as hurricanes 24 hours a day.
- Disadvantages:
- It takes longer for the signal to get to earth and back to satellite (Delay of .22 s).
- Increased difficulty of telephone conversations.
- GEOs are not positioned in the farthest northern and southern orbits.
Ref : Google Images
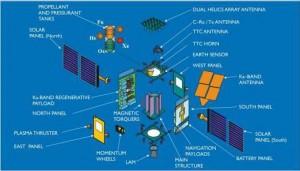
Satellite Components :
Bus Mainframe :
It is the frame of the system. It contains antenna dishes, transponders, thrusters, fuel cylinders, engine, position control system,solar panels etc. It is made of aluminium and carbon fibre.
Command Control and Telemetry :
The station from earth monitors the health of satellite including its vital parameters continuously which ensure the satellite is operable for many years. They have a separate antenna and separate frequency to monitor and establish radio diagnostics and control (RDC).
Power System :
Photovoltaic cells are employed on solar panels which have a conversion rate of 20%.They power up the circuitry on board and recharge batteries. The panels are foldable and are constantly positioned for maximum collection of sunlight on panels. Apart from that on board Ni-Cd batteries that have best power weight ratio and are used on eclipses, where shadow of the planet causes block in sunlight.
Orbital Position System:
The gravitational fields of earth and moon have effect on the orbit of the satellite. The fuel in satellite system, hydrazine is thrusted out to maintain on its elliptical path (Attitude Control System). The attitude and orbit control subsystem consists of sensors to measure vehicle orientation; control laws embedded in the flight software; and actuators (reaction wheels, thrusters) to apply the torques and forces needed to re-orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, keep the satellite in the correct orbital position and keep antennas positioning in the right directions.
Antenna and Receivers :
Every satellite has got a different range of antennas on it. Medium gain antenna , high gain antenna etc. are employed for various purposes. Different radiating power is needed for these antennas.LEO satellites need big antenna dish because of low power and low frequency and due to high frequency range of GEO satellites, need a small antenna system. They have carbon fibre skins bound on Kevlar honeycomb. They don’t have a smooth surface.
The Thermal Control Subsystem
The thermal control subsystem helps protect electronic equipment from extreme temperatures due to intense sunlight or the lack of sun exposure on different sides of the satellite’s body (e.g. Optical Solar Reflector).Vacuum deposited aluminium on kapton is used for thermal insulation too.
Transponder :
The second major module is the communication payload, which is made up of transponders. A transponder is capable of :
- Receiving uplinked radio signals from earth satellite transmission stations (antennas).
- Amplifying received radio signals
- Sorting the input signals and directing the output signals through input/output signal multiplexers to the proper downlink antennas for retransmission to earth satellite receiving stations .
After serving its term the small thrusters fire off the satellite using the last of on board fuel to its graveyard orbit away from earth in to the deep space.

Ref : Google Images