– by Aman Pandey
What does the path consist?
The goal of this article is to let you know about a BASIC BLOCKCHAIN structure by making a sample blockchain by using a Scripting language Python.
And a small assignment at the last.
The information about the following will be provided on the further articles:
-
- various applications of blockchain and at various levels
-
- use blockchain to create your own cryptocurrency
- use of blockchain to create a file deployment system
and Many More…
This article will, for right now, will not have information about deploying your own Blockchain Application, and creating a distributed and decentralized file sharing system.
If you are just interested with how to create a blockchain Jump directly to CONSTRUCTING even I would have done that…
So, let’s start to learn something new……
What is Blockchain?
Back in 2008, some mysterious Person/group of persons named SATOSHI NAKAMOTO released a whitepaper named Bitcoin: A Peer to Peer Electronics Cash System (I suggest that you read the paper to understand how it was presented to the world) in which BITCOIN was described to be a BLOCKCHAIN based technology,
-
- a completely trustless (though the meaning is exactly the opposite, it actually means no trust issues)
-
- Distributed
-
- Decentralised
- and, Encrypted
technology that can actually serve as a new form of currency which has its value just as a Stock Share and transaction just like a Barter system.
So, right now before turning this article into a History(story) or market revolutionalizing technology journey let’s start some keyboard ticking and see where we are able to implement key points of a Blockchain, though I will provide you enough resources to read more about emergence and have an intuitive idea about its potential.
Let’s get started…
Design and Features
So, let us begin with the basic design of blockchain by understanding how does it implement its key features.
Before explaining further I want you to go through this wonderful video about blockchain. So we shall jump directly to the technical part. It will let you understand most of the things.
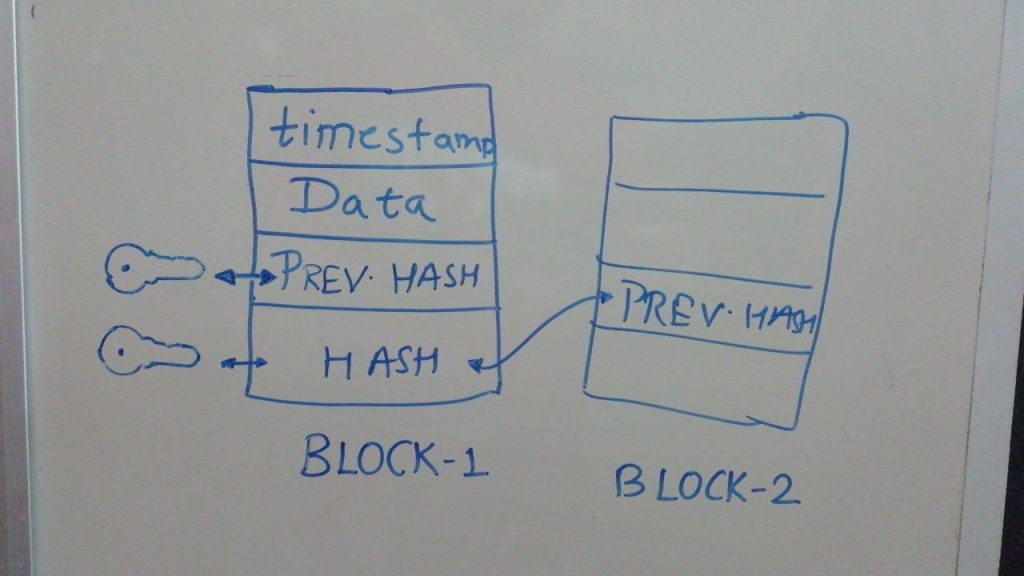
Now after this you must have understood the basic structure of Blockchain.
It is a distributed and decentralized ledger system which provides a TAMPER free service to store records.

Image Source: https://i.stack.imgur.com/hDDzg.png
Constructing:

Prerequisites:
-
- Python 3.6 (a basic python would work but if you don’t know any about it don’t worry it’s very simple and I will try to give an intuitive idea about what I am using and why.)
-
- a cool text editor would work well
> Sublime Text 3 (choose according to the platform you have, it’s lightweight and good)n
> Atom (the best one to use, has an extension for a terminal)
- a cool text editor would work well
-
- LINUX (Suggested, It’s better to switch to Linux now if you really have to do some good) ……that’s it for now, its basic
Let us start by creating a BLOCK:
-> BLOCK:-
We’ll start by creating a class of simple BLOCK using Python:
class block:
def __init__ (self, timestamp, data, previousHash = ' '):
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.data = data
self.previousHash = previousHash
self.hash = #TODO function calculateHash()
Just have a look at this block we have 4 arguments. Of course, self is working for self-element initialization, for those who don’t understand just understand that it is a kind of PYTHON convention of constructors.
Also that we haven’t included hash in the block argument as it will be calculated and stored inside the function itself #TODO.
Now let’s write the function to calculate hash the block:
def calculateHash(self):
return sha256((str(self.timestamp) + str(self.data) + \
str(self.previousHash).encode()).hexdigest())
Now, few points to note here are
-
- use of encode() and in the return line hexdigest()
→ so the answer for that is you need to encode every text before hashing, I’ll try to cover it in further blogs.
→ and to convert hash object into a string we need to use the hexdigest function
- use of encode() and in the return line hexdigest()
-
- and yes, for sha256 you need to import hashlib library, and also you need to convert everything into a string before hashing it
- Also, we need to include time for timestamp
So the code for blocks looks like: –
from hashlib import sha256
import time
class block:
def __init__ (self, timestamp, data, previousHash = ' '):
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.data = data
self.previousHash = previousHash
self.hash = # TODO
def calculateHash(self):
return sha256((str(self.timestamp) + str(self.data) + \ str(self.previousHash).encode()).hexdigest())
and now let’s begin with our Blockchain class definition:
-> BLOCKCHAIN:-
Genesis Block: the very first block of the blockchain is termed as a genesis block. And it generally can have any data. So we need to initialize our blockchain with it if we don’t have any block in the BLOCKCHAIN. We will have the following structure:
Data → “genesisBlock”
previousHash → “00000”
class blockchain:
def __init__(self):
self.chain = [self.createGenesis()]
def createGenesis(self):
return block(time.ctime(), "genesisBlock", "00000")
So this is our blockchain which gets initialized with a list named chain, everytime a new class object is created. We’re still having some functions to add to it.
-> MINING:-
Whenever a new transaction is made, and a new block is created and added to the blockchain, the complete process is termed as mining.
As to make blockchain simple for this very first blog, I am not going to put any complex mining functions and verification algorithms for now. Just deal with simple mining.
So, the mining functions will be having to take input from the user and create a block/node for it.
So, before making mining, we have to deal with taking the user’s input and start mining:
- Starting a Blockchain
-
CEVcoin = blockchain()
- Taking user input and creating a block
-
data = input()
- Writing mineBlock():
This function is the part of the blockchain so has to be written inside blockchain. Hence our code with the function of adding nodes looks like:
from hashlib import sha256
import time
class block:
def __init__ (self, timestamp, data, previousHash = ' '):
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.data = data
self.previousHash = previousHash
self.hash = self.calculateHash()
def calculateHash(self):
return sha256((str(self.timestamp) + str(self.data) + str(self.previousHash).encode()).hexdigest())
class blockchain:
def __init__(self):
self.chain = [self.createGenesis()]
def createGenesis(self):
return block(time.ctime(), "genesisBlock", "00000")
def mineBlock(self, data):
node = block(time.ctime(), data, self.chain[-1].hash)
# mining a new block to the blockchain
self.chain.append(node)
CEVcoin = blockchain()
data = input()
# sending data to get mined
print(“\n\nMining new block……..”)
CEVcoin.mineBlock(data)
*do note down the self.calculateHash() application in def __init__ function of block
Well, this the BACKBONE of every BLOCKCHAIN.
Its applications are at many places. Bitcoin is one of them. Refer links at the bottom for them.
One last thing I’ll do is to print the Blockchain we just made:
def printBlockchain(self):
for i in range(len(self.chain)):
print("\n-----Block ", i ,"---------\n timestamp = "\
, self.chain[i].timestamp,"\n data = ", \
self.chain[i].data, "\n previousHash = ",\
self.chain[i].previousHash,"\n hash = ", \
self.chain[i].hash)
Just add it inside the class blockchain().
And here, you are done with your first blockchain cryptocurrency
For complete CODE refer : https://github.com/johnsoncarl/Blog-CEVcoin
*i’ll add more blogs with its applications like
- Making a ledger system
- Making your own cryptocurrency
- Regarding P2P network based blockchain
**Please do like & share this blog if you really like it. And comment if any doubts.
Blog by:
2nd Year, Civil Engineering, SVNIT.
You can also have a look at my team Project with Ujjwal Kumar – LinkedIn & Hrishabh Sharma – LinkedIn, another CEV members @ Rajasthan DIGIFEST 2k18 Online hackathon – a 36 hours hackathon held on 6 July 2018 on making a cryptocurrency RAJCOIN for Rajasthan Govt @ the following Github link.
https://github.com/Sharma-Hrishabh/digifest2k18
You need to follow the complete instructions given in readme. SO, KEEP PATIENCE.
Extra Resources to read:
- Forbes – A Very Brief History Of Blockchain Technology Everyone Should Read
- Blockchain Glossary: From A-Z
- Forbes – Blockchain as an Application Platform
Assignment:
Now the assignment is that, make your own crypto coin and mail the code as a zip file to my email id aman0902pandey@gmail.com.
**you can ask any doubts regarding this @ the email address provided above.
Please give a thumbs up and share if you really like the blog.
NOTE: this is only for Educational purposes and not for commercialization.
Cheers…
