INTRO:
Let us put on the table first what makes it important to immediately shift our attention to cope blackouts by analysing what destruction it is capable of.
We are guided by one question: What is the core reason for blackouts?
Are they technical fault or it is intentionally caused by few bloody minds to create outrage against a whole society or a country.
The answer is both.
There were many cases when the electrical system itself failed to keep up, either due to overloading, or some faults like birds tangling on lines, trees falling, etc.
And there were also cases where a group of wicked hackers with a simple machine called laptop caused the whole system to collapse and brought the modern urban society on knees. This terrifying act of spreading wide outrage in cities, part of countries and even the whole country are called a “CYBER ATTACK”. Some nation considers cyber attacks more outrageous than ballistic or even a nuclear missile attack.
A doomed shut down of power plants across the nation can typically lead to the following consequences:
In the early hours of the attack, all the passenger on electrified transportation system will come to immediate rest. Trains and metros in remote locations, over the bridge, under a tunnel and all the other possibilities will only leave the passengers in turmoil.
Industries like manufacturing, packaging will be brought down causing an exponential rate of increase in financial losses. Soon houses will consume all its battery backups and important gadgets like fridge, fans, coolers, AC, lights, computer all will come to zero.
Important and critical systems like communication system, major cooling systems, all will come to halt. Services like water availability, sewage treatment plants, incarnation plants, hospitals, ATMs, banks, etc one by one will come offline.
Now imagine yourself stuck in this situation, what would you do?
Can you imagine the loss of lives, property and other things? In this way, a city can be turned to a cremation ground in a matter of a few days.
History has been the greatest proof of destruction it is capable to cause. The Ukranian Blackout of 2015, Indian Blackouts of 2012 and 2001, the American and Italian Blackout of 2003, 1999 Blackout in Brazil are names of few. Nations around the globe consider grids as a delicate string of urban lifeline and thus show huge concern about it.
We all know that the world would never see another Great London fire of 1666, but we cannot forget it. The urban fire safety system is the aftermath of that catastrophe, but revisiting the event, we might come up with solutions which could be more viable and promising than existing ones. Similarly, let us take the two most typical cases of blackouts, and try to analyse the incidents.
CASE 1: North Indian grid failure of 2012
At the end of July 2012, the nation witnessed two back to back largest blackouts in its history. Those two blackouts debunked the weak and incompetent condition of Indian Power Grid to manage increasing load demand, on the other hand, opened up opportunities to work for the vulnerability of the grid to failure in future.
WHAT HAPPENED?
30th July 2012:
- On 30 July 2012 at 0233 Hrs a disturbance in the Northern Regional Grid lead to a blackout, covering all 8 states that include Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, and Chandigarh.
- Nearly 300 million which then was about 25% of Indian populations was affected.
- Monday morning hours were accompanied by non-operational trains and traffic signals. Several hospitals, water treatment, refineries were shut.
- The supply to Railway stations and airports were extended only by 0800.
- The Northern Regional System was fully restored by 1600 Hrs.
31st July 2012:
- Another disturbance occurred at 1300 hours of 31 st July 2012 affected the Northern, Eastern and North-Eastern Regional grids, that caused blackouts in 21 states.
- Nearly 600 million which was 50% Indian population was without power in peak heat season.
- More than 300 trains were cancelled, around 200 miners were trapped in eastern India as lift failed, vehicular traffic-jammed and many critical services were affected.
- Power supply to emergency loads like Railways, Metros and airports were mostly provided by about 1530 hours.
- The system was restored fully by about 2130 hrs of 31 st July 2012.
The topmost organisation of power grid the CEA (Central Electricity Authority) came up with reports on what caused the failure and with suggested measures to check such cases in future. All of them have been well implemented and it seems that our power grid had become more resilient. A blog on the same is not at all needed as every minute detail can be accessed online, but the point is to analyse the event and extract lessons for ourselves.
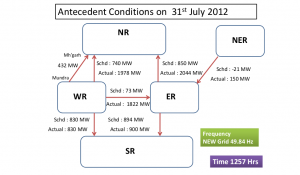
Here are some antecedent parameters of three main elements of the grid that gives us clues that what triggered the shut down that day of 31st July.
Load Quantum and distribution:
2012 saw a failed monsoon in Northern Indian. Also, end of July marks the peak summers, and each section grid in these seasons works at its maximum capability to supply for farmer’s heavy-duty submersible pumps and household’s ACs, coolers and fans.
Similar were conditions in Eastern Regional grids also. However, coastal regions of Western and Southern Regional grids were at low to moderate loads.
Transmission:
By the year 2006 the NR, ER and NER were synchronized at 50 Hz to form so-called NEW grid, and in 2012 grid authority were preparing to synchronise Southern Grid with the NEW grid under the govt scheme of one nation and one grid. The Grid was in a phase of expansion and transformation, laid regulation were loosely followed and the grid was not capable of significant powers transfer among the different regional grids.
Also, many major lines were under construction work or offline due to other reasons. For eg 400 kV Bina-Gwalior (2). List of all the transmission links faulty on that day is given in report no 4 in reference in the end.
Generation:
As grid was under expansion some new power stations were running under test, like the Sipat Thermal Power of Western Regional Grid. Actually, the western region was surplus in power generation due to low load demand in the west.
Whereas some thermal and gas power stations in NR were in outage due to unavoidable reasons like coal/gas shortage, under-requisition by stakeholders. Some hydro-stations were experiencing an outage due to high slit due to summers eg Vishnuprayag HPP.
Following is the generation and load demand at 1257:
POWER FLOW AT 1257 HOURS:
The antecedent status of load, transmission and generation resulted in power flow as given below:
The scheduled load demand in NR was 2022 MW but the actual withdrawl was unexpectedly high at 4454 MW. The huge quantum difference in power consumption was all withdrawal from other power surplus regions thereby enormously stressing the inter-regional transmission links.
AND THE LARGEST EVER “BLACKOUT” BEGINS…….
- At 13:00:13 Hrs the important high capacity 400 kV BINA-GWALIOR link, directly transferring power from WR to NR grid tripped. This event was followed by the greatest drawback of any synchronised grid, “the cascading effect”.
- Separating the Gwalior region from WR grid, it continued to get supplies via the 400 kV Agra- Gwalior link. This resulted in a change in the power flow direction, and massive power diverted to NR from WR via WR-ER-NR route, immediately stressing them and tripping them also.
- Followed by these inter-regional trippings the power transfer was hammered.
- The power surplus Western Regional grid’s frequency overshot immediately to 51.46 Hz, triggering regional tripping. The over speeding alternators one by one isolated from grid and WR followed a blackout.
- The enormously power deficit Northern Regional grid’s frequency immediately settled to 48.12 Hz. The slowed alternators were cut-out by control and feedback system and this grid also experienced a blackout. ER and NER followed the same fate.
- Southern Regional Grid importing 2000 MW power from the NEW grid through the Talcher-Kolar HVDC bipole link saw a decline in frequency down to 48.88 Hz from 50.46 Hz, and also saw many alternators going offline.
And by 13:00:19 all of this had happened on that day, and India witnessed the massive blackout covering 21 states and affecting 600 million end customers.
FAILURES:
Let us analyse what exactly went wrong and what could have done to avoid that:
- Firstly the Load forecasting went severely inaccurate for the NR and ER grids, thereby caused situations that required immediate follow back steps, like load shedding.
- Various defence mechanism like UFR (Under Frequency Relay), rate of change of frequency relay were, etc failed to execute load shredding that could have helped escape that blackout.
- However, on the other hand, the surplus power generating WR grid injected the required quantum power through the inter-regional links and continued to do so even when the capacity of links was far exceeded from the rated.
- Various power plants like under test Sipat TPS continued injecting the unscheduled power even after the WRLDC issued a verbal and written message to lower the plant output.
- The investigating team also suggested significant reforms in communication and SCADA system implementation.
CONCLUSION:
The Grid indiscipline and inability to strictly follow the laid regulation, inaccuracy in forecasting and failure of the protection systems were the reason for the blackout.
The investigation team came with measures to further check the occurrence of such events like reviewing the transfer capability of important inter-regional links, special protection systems, effective enforcement of rules and strict action against the rule breakers, etc.
THE BLACKOUT OCCURRED IN 2012, ISSUES HAS BEEN ALREADY FIXED, THEN WHY THE HELL WE STUDIED THIS??????
And certainly, this is the most urgent question to answer.
The most crucial lessons to understand is operational discipline. This event set an example of how to defy the institutional rules and regulation can be followed by a catastrophe, that has an impact on such a large scale. So, engineers, workers and executives must understand the responsibility of their jobs, and consequences if they fail to perform.
The technical lesson to be extracted is that all the engineering system like electric grids, internet, transportation systems, need always to be under the cycle of continuous improvement and evolution to improve for better and safe. Maybe the SPS needs to be reviewed again considering the current load demand, links capacity to be increased, and the rules to be applied more strictly.
CASE 2: Ukrainian Grid Cyber Attack of 2015:
INTRODUCTION TO CYBER ATTACKS ON GRID:
Accommodation of renewable energy and continuously meeting the dynamic load demand on the grid requires the grid to push for modernisation by enabling remote access capability to centrally and effectively distribute power from surplus to deficit region. The recent overpaced development of electronics has opened up opportunities to equip the grid with all the superpowers like HVDC, SCADA, and many other IP-based digital technologies.
But this is not at all time to relax and chill. Smart grid technologies litter the grid with endless security vulnerabilities and flood the grid with numerous threats, and thus present very complicated and worse glitches to deal with. Hackers have a whole lot of techniques in their quivers to get into the system to bring it down.
The world was aware of all these threats but witnessed for the first time the ravage of a cyber attack on an electric grid that caused a power outage on 23 Dec 2015 in Ukraine.
The attack was a professionally-planned, well resourced, highly synchronised, multistage, multisite, had long-lasting aftermaths. (Each term will be explained)
WHAT HAPPENED?
On 23rd Dec 2015, at 3:35 PM (local time) three power distribution companies were targeted and adversaries were successful to de-energized seven 110 kV and twenty-three 35 kV substations for three hours leading to 225000 end users without power in December-end winter. The outage came as a result of third-party entry into the company’s computer system, SCADA, ICS (Industry Control System), etc.
Three other organizations, from other critical infrastructure sectors, were also breached but did not experience operational impacts.
ATTACK WALK THROUGH:
Following is the timeline events of the attack, which gives us an idea of what vulnerabilities a Smartgrid is subject to:
- RECONNAISSANCE: The intelligence gathering, planning and preparation for the attack is estimated to well started in or before May 2014. Active reconnaissance like spying and direct interaction with employees and passive reconnaissance like open-source IG have yielded attackers information like the type of technology deployed, associated vulnerability, possible attack vectors, hardware model, operating system in workstations, etc.
- WEAPONIZATION: Analysing the vulnerabilities of the system an appropriate malware was developed and the delivery mode was selected. They used weaponised MS Word and MS Excel by embedding malware named Blackenergy-3, which get installed in operator machines as they enable macros script to view the content.
- DELIVERY: The spear-phishing technique was used in the campaign to deliver malware on such a large scale. Reports say various other malwares were also discovered like GCat, Dropbear, etc in other sectors like railways, etc.
- ESTABLISH A CONNECTION: The BE-3 works by modifying internet settings to establish a persistent control and command connection to an external server and give unauthorized access to system data.
- HARVEST CREDENTIALS: The BE-3 was capable of receiving a range of commands from the external server like download, upload, install, uninstall, execute, update configuration, etc. The attacker used BE-3 to acquire the employee credentials by a wide range of methods like keylogging and targeting password managers.
- LATERAL MOVEMENT: BE-3 also helped the attackers in internal reconnaissance, helped them to identify targets and discover the whole network and navigate them into ICS network from the corporate network, which gave them access to HMI (Human Machine Interface) and field device control.
- VPN GATEWAY: Access to VPN (Virtual Private Network) credential allowed attackers to gain remote access to corporate and ICS along multiple lines as well as reduced the visibility of malicious activity.
- TARGET IDENTIFICATION: HMI workstations, data centre servers, control centre UPS, serial-to-Ethernet converters, and the substation breakers were selected to attack sequentially.
- ATTACK PREPARATION: At this stage of attack they began developing malicious firmware to update the already installed healthy old firmware on ICS operator system, which was coded to execute after reboot or on some trigger. Investigators clearly stated that such a successful execution of such a high level of malicious firmware updates are only possible by continued capability testing which requires their own system for assessment, which indicated the state-sponsored cyber-attack.
- DATA DESTRUCTION MALWARE: Alongside the firmware update to trip the breaker, they upload the networked system with malware called killdisk to erase all the history logged before the attack to avoid being traced and analyse how it happened.
- TDOS ATTACK: In the Telephony denial of service the attacks managed to generate fake calls and flooded the service centre to actually stop affected from reporting to the company.
- SCHEDULE UPS SHUTDOWN: In this case of Ukraine distribution system the UPS were also networked hence the attackers also hijacked them to stop the critical system like telephony and data centres to operate after the tripping, hence increasing the time for recovery.
AND THE ATTACK BEGINS…..
After prolonged recon, clandestine access and so much preparation the attackers on 23rd December 2015 at 1515 Hours (local time) the attackers by remote access took complete control of the system in the substation of three Ukrainian DISCOMS. In some cases, the updated firmware began tripping the breakers automatically whereas in some cases phantom mouse was used. (The operator in the control room watched the cursor tripping the breakers without even him touching his own mouse). TDOS attack eliminated the possibility to get what is happening on the ground as the telephone lines got jammed with fake calls. After tripping breakers in 57 sub-stations, the Killdisk came to action by erasing the data of the system. Before wrapping up the passwords of some user were changed to check them ever entering the system, the updated firmware left some of the devices impossible to recover ever. UPS went down as scheduled and the operators were left with no option to gain remote access over their field devices hence the breakers were manually closed individually which took nearly six hours.
No doubt that this attack has been logged in history of power grid industry as a one of evilest professionally-planned, well resourced, highly synchronised, multistage, multisite attack.
FAILURE POINTS:
- No active network security measure to check malicious activity once intruder gets into the system, this would have easy ruled out the possibility of nearly year-long recon which was the core step in intelligence gathering and final execution.
- No two-factor authentication for the VPN access into the ICS network.
- No frequent change in passwords by the employees and unaware of been trapped by spear-phishing, etc.
- No two-step verification for even critical firmware update.
- Exposing critical data on open-source like company website, etc.
TAKEAWAYS:
What is astonishing is not the professionalism of the attackers in so well planning and execution of each step i.e. spear-fishing, malware and firmware development, harvesting credentials, scheduling UPS, TDOS, etc but it was their ability to study the whole system by recon, aided with BE – 3, without being traced for so long time. What happened in Ukraine was a perfect combination of very odd possibilities that the world might never see again. But surely attack present in front of us how a system that appears impenetrable can be hijacked on grounds of minute elementary flaws, human negligence and unprofessionalism.
LESSONS FOR INDIAN GRID:
Here comes the part for which we follow through two mammoth disaster analysis. However, our grid has undergone many reforms after the 2012 failure and has become more resilient after pushing the grid for
- synchronisation of all regional grid.
- Smart Grid gives the remote operation capability and significantly increases
- Reliability: by lowering the time for fault detection and hence recovery.
- Efficiency: using renewables
- Economy: better resources management
However, it would immature to talk about the benefits of ‘Smart Grid’ without considering the threats it creates. Also, the level of skills and sophistication showed by attackers in 2015 attack alarms all the grid operator across the world to keep a step forward in preparedness to cope with them.
In the attack of 2015 distribution utilities were on target if it had been generation or transmission then certainly aftermath would have exponentially disastrous. The American test experiment called Aurora Vulnerability, in which the computer malicious firmware trip the circuit breakers and instantaneously closed pulling the generators in plants out of phase. And in a synchronised grid like that of India, nothing could more fatal than a generator of even one plant going out of phase with the grid. Immediate explosion and cascading failure would be the consequence.
LAST WORDS:
Unfortunate but it is true that there is no such thing as absolute security. If there is a capable attacker with the correct means and motive, the targeted utility can never be protected enough. Total elimination may never be possible but surely damage can be kept at the minimum.
Strong communication protocols, multifactor authentication, continuous network security monitoring, and cyber-threats awareness are some of the areas which must be always evolving with time to keep the grid safe and customers happy!
REFERENCES:
Numerous reports have been taken into account while studying what happened on 31st July 2012 and on 23rd December 2015:
- https://ics.sans.org/media/E-ISAC_SANS_Ukraine_DUC_5.pdf
- http://web.mit.edu/smadnick/www/wp/2016-22.pdf
- https://www.boozallen.com/content/dam/boozallen/documents/2016/09/ukraine-report-when-the-lights-went-out.pdf
- http://www.cercind.gov.in/2012/orders/Final_Report_Grid_Disturbance.pdf
Keep reading, keep learning!
TEAM CEV!!