What do we first mean by “Security”?
“The quality or state of being secure—to be free from danger.” A successful organization should have multiple layers of security in place:
• Physical security: safeguarding personnel, hardware, software, networks, and data against physical actions and events that could result in significant loss or damage to an enterprise, agency, or institution.
• Operations security-Protection of the details of a particular operation or activity.
• Communication Security-Protection of organization communication media, technology, and content
• Network Security-Protection of Networking components, connections and contents.
• Information Security-Protection of information and its Critical elements.

Information Security
Information security refers to securing the data or information and information systems from unauthorized access, unauthorized use, misuse, destruction, or alteration. It plays a vital role in protecting the interests of individuals who depend on information or data. Information security aims to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.

Elements of Information Security
Confidentiality:
Information is accessible only to those who are authorized to view it.
Integrity:
Information, especially while being communicated, is protected against unauthorized modification.
Availability:
Information is invulnerable to attacks or is recoverable in a secured way, i.e., it is available (only to authorized) when it should be.
Non-Repudiation:
The sender of information cannot deny that information has NOT been sent by him.
The Need for Information Security
-Protecting the functionality of the organization
-Enabling the safe operation of applications
-Protecting the data that the organization collects and uses
-Safeguarding technology assets in organizations
The Importance of Information Security
Companies need to be confident that they have strong data security and that they can protect against cyber-attacks and other unauthorized access and data breaches. Weak data security can lead to key information being lost or stolen, creating a poor experience for customers that can lead to lost business and reputational harm if a company does not implement sufficient protections over customer data and information security weaknesses are exploited by hackers. Solid information security reduces the risks of attacks in information technology systems, implements security controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, prevents service disruption caused by cyber-attacks such as denial-of-service (DoS attacks), and much more.
Information Security Attack Vectors
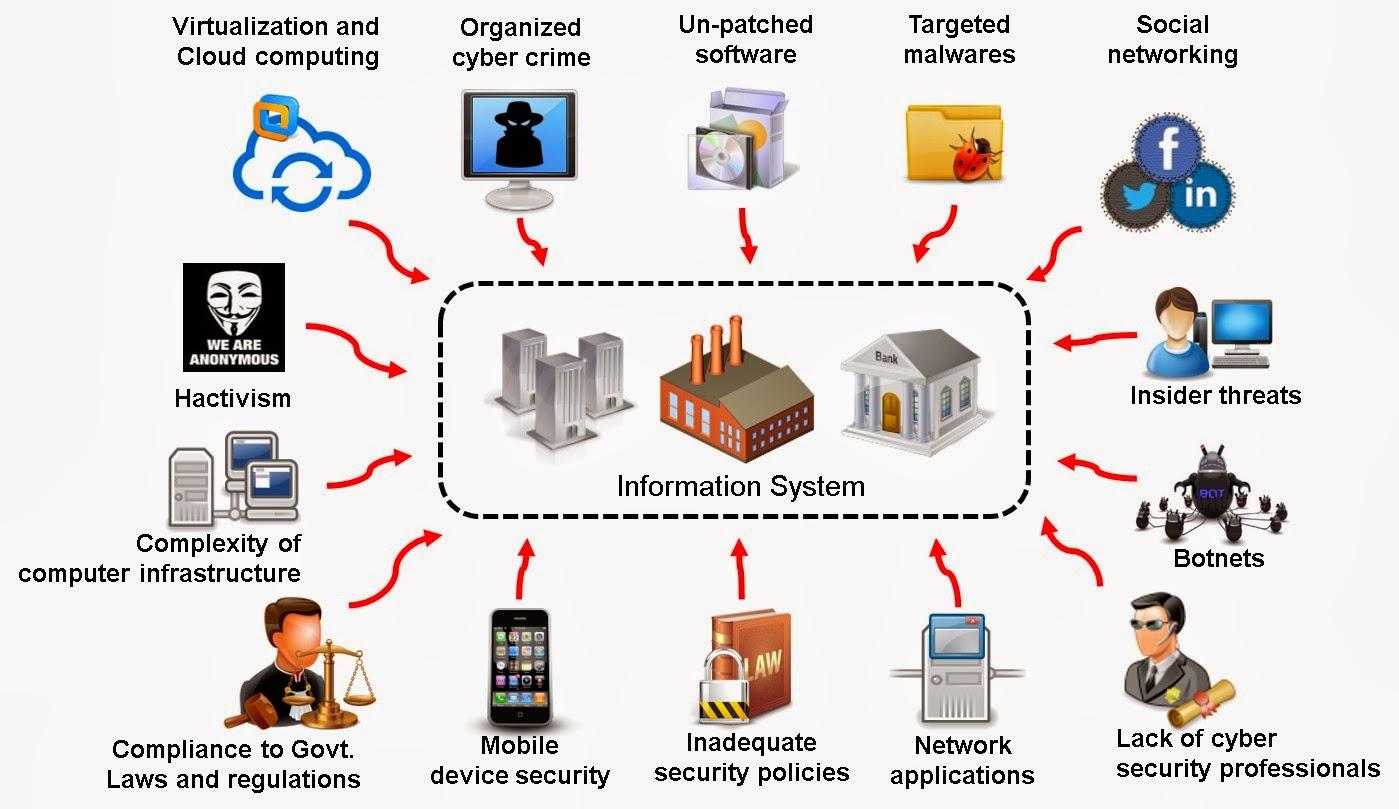
An attack vector is a pathway or method used by a hacker to illegally access a network or computer to exploit system vulnerabilities. Hackers use numerous attack vectors to launch attacks that take advantage of system weaknesses, cause data breaches, or steal login credentials.
Cloud Computing Threats:
Cloud computing is an on-demand delivery of IT capabilities where sensitive data of organizations and clients is stored.
The flaw in one client’s application cloud allows attackers to access other clients’ data.
Advanced Persistent Threats:
An APT is an attack that focuses on stealing information from the victim’s machine without the user being aware of it.
Viruses and Worms:
Viruses and worms are the most prevalent networking threats that are capable of infecting a network within seconds.
Mobile Threats:
The focus of attackers has shifted to mobile devices due to the increased adoption of mobile devices for business and personal purposes and comparatively lower security controls.
Botnet:
A botnet is a huge network of compromised systems used by an intruder to perform various network attacks.
Insider Attack:
It is an attack performed on a corporate network or a single computer by an entrusted person (insider) who has authorized access to the network.
Information Security Threat Categories
Network Threats
-Information gathering
-Sniffing and eavesdropping
-Spoofing
-Session hijacking and Man-in-the-Middle attack
-DNS and ARP Poisoning
-Password-based attacks
-Denial-of-Service attack
-Compromised-key attack
-Firewall and IDS attack
Host Threats
-Malware attacks
-Footprinting
-Password attacks
-Denial-of-Service attacks
-Arbitrary code execution
-Unauthorized access
-Privilege escalation
-Backdoor attacks
-Physical security threats
Application Threats
-Improper data/input validation
-Authentication and Authorization attacks
-Security misconfiguration
-Information disclosure
-Broken session management
-Buffer overflow issues
-Cryptography attacks
-SQL injection
-Improper error handling and exception management
Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity is the protection of internet-connected systems such as hardware, software, and data from cyber threats. The practice is used by individuals and enterprises to protect against unauthorized access to data centres and other computerized systems.
Distinctions between Cybersecurity and Information security

Cybersecurity is meant to protect against attacks in cyberspace such as data, storage sources, devices, etc. In contrast, information security is intended to protect data from any form of threat, regardless of analogue or digital. Cybersecurity usually deals with cybercrimes, cyber fraud, and law enforcement. On the contrary, information security deals with unauthorized access, disclosure modification, and disruption.
Cybersecurity is handled by professionals who are trained to deal with advanced persistent threats (APT) specifically. Information security, on the other hand, lays the foundation of data security and is trained to prioritize resources first before eradicating threats or attacks.
Information Security Laws and Standards
• Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS)
• ISO/IEC 27001:2013
• Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) 1996
• Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) 2002
• The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) 1998
• Federal Info Security Management Act (FISMA) 2002
• Cyber Laws
Conclusion
In conclusion, nowadays the value of data has reached a critical point, becoming one of the most important assets that a company can possess, while collecting, processing, transmitting, and storing it has become too complex.
Information security is designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of computer systems and physical data from unauthorized access, whether with malicious intent or not.
Confidentiality, integrity, and availability are referred to as the CIA triad.
Every information security program is concerned with protecting the CIA triad while maintaining organizational productivity.
“The goal of information security is not to bring residual risk to zero; it is to bring residual risk into line with an organization’s comfort zone or risk appetite.”
