We all have witnessed this technology for downloading our favorite movie which wasn’t available elsewhere. It is one of the most impeccable techs in the world of data sharing ever thought and brought to reality by a human.
Definition
“BitTorrent is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P) which is used to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a decentralized manner.”
The protocol came into existence in 2001(thanks to Bram Cohen) and is an alternative to the older single source, multiple mirrors (user) sources technique for distributing data.
A Few terms
- BitTorrent or Torrent: Well, BitTorrent is the protocol as per its definition, whereas Torrent is the initiating file which has the metadata(source) of the file.
- BitTorrent clients: A computer program that implements the BitTorrent Popular clients include μTorrent, Xunlei Thunder, Transmission, qBittorrent, Vuze, Deluge, BitComet, and Tixati.
- Seed: To “seed” the file denotes to “download” the file.
- Seeding: Uploading the file by a peer after their downloading is finished.
- Peer: (The downloader) Peer can refer either to any client in the swarm or specifically to a downloader, a client that has only parts of the file.
- Leecher: Similar to peer, but these guys have poor share ratio i.e. they doesn’t contribute much in uploading but only download the files.
- Swarm: The group of peers.
- Endgame: an applied algorithm for downloading the last pieces of any file. (Not the Taylor swift’s Endgame).
- Distributed Hash Tables(DHTs): A decentralized distributed system. In layman language, hash tables are used to provide encryption using something similar to lock and key model.
Working
Let’s have the gist of what happens while torrenting.
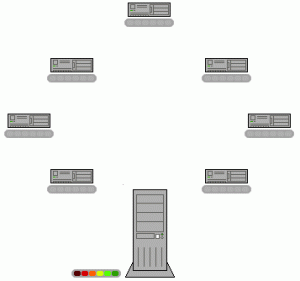
The following GIF explains this smoothly.
First, the server sends the pieces(colored dots) of the files to a few users(peers). After a successful download of a piece of the file, they are ready to act as a seeder to upload the file to other users who are in need of that file.
As each peer receives a new piece of the file, it becomes a source (of that piece) for other peers i.e., the user becomes seeder, giving a sigh of relief to the original seed from having to send that piece to every computer or user wishing a copy.
In this way, the server load is massively reduced and the whole network is boosted as well.
Once a peer is down with downloading the complete file, it could in turn function as a seed i.e. start acting as a source of file for other peers.
Speed comparison:
Regular download vs BitTorrent Download
Download speed for BitTorrent increases with an increase in peers joining to form the swarm. It may take time to establish connections, and for a node to receive sufficient data to become an effective uploader. This approach is particularly useful in the transfer of larger files.
Regular download starts promptly and is preferred for smaller files. Max speed is achieved promptly too.
Benefits over regular download
- Torrent networking doesn’t depend on the server being distributed among the peers. Data is downloaded from peers which eventually become seeds.
- Torrent files are open source and ad-free. An engrossing fact about the same is that TamilRockers use torrent to act as the Robin hood for pirated movies and songs, which is apparently an offensive act.
- Torrent judiciously uses the upload bandwidth to speed up the network: after downloading, the peers’ upload bandwidth is used for sending the file to other peers. This reduces the load on the main server.
- A File is broken into pieces that helps in resuming the download without any kind of data loss, which in turn makes BitTorrent certainly useful in the transfer of larger files.
Torrenting or infringing?
Using BitTorrent is legal. Though, Downloading copyrighted material isn’t. So torrenting isn’t infringing.
Most BitTorrent clients DO NOT support anonymity; the IP address of all peers is visible in the firewall program. No need to worry though, Indian govt. has clarified that streaming a pirated movie is not illegal.
Talking about the security concerns, each piece is protected by a cryptographic hash contained in the torrent descriptor. This ensures that modification of any piece can be reliably detected, and thus prevents both accidental and malicious modifications of any of the pieces received at other nodes. If a node starts with an authentic copy of the torrent descriptor, it can verify the authenticity of the entire file it receives.
Further Reading:
IPFS is not entirely new but is still not widely used.
Read it here on medium.
Written by Avdesh Kumar
Keep Thinking!
Keep Learning!
TEAM CEV